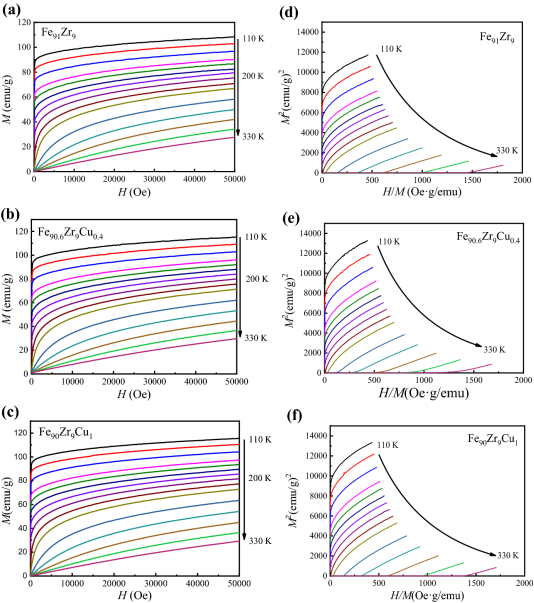
In this work, low-temperature magnetic properties and magnetocaloric properties of Fe91−xZr9Cux (x = 0.0, 0.4 and 1.0) amorphous ribbons were investigated. It was found that the Curie temperature (TC) of the ribbons increases with Cu content from 210 (for x = 0) to 218 K (for x = 0.4), and decreases to 214 K with the further of 1.0% Cu. The values of the maximum magnetic entropy change (− ΔSM)max were found to be 2.63, 2.75 and 2.88 J kg−1 K−1 for the Fe91−xZr9Cux (x = 0.0, 0.4 and 1.0) amorphous ribbons, respectively, under the field of 50 kOe. The corresponding refrigeration capacity (RC) values of the Fe91−xZr9Cux (x = 0.0, 0.4 and 1.0) amorphous ribbons are 114, 121 and 120 J kg−1, respectively. These values are comparable to those obtained for the previously studied ternary Fe-based amorphous alloys. These results demonstrate that an appropriate amount of Cu substitution can enhance the (− ΔSM)max and RC of Fe-based amorphous alloys. These Fe-based amorphous alloys are promising for application as low-temperature magnetic refrigerants and multi-functional materials.
文章链接:Journal of Low Temperature Physics. 2020, 200: 51–61.